Article: Before there was SPF, there was Siberian Pineapple
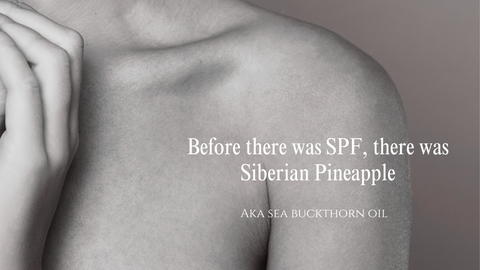
Before there was SPF, there was Siberian Pineapple
Sea Buckthorn berries, scientifically termed Hippophae rhamnoides, have long been revered for their exceptional wound healing properties. Packed with bioactive compounds such as flavonoids, phenolic acids, vitamins C and E, and omega fatty acids, Sea Buckthorn extract stands out for its ability to expedite the wound healing process. Asif et al. (2011) showcased its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and regenerative effects on damaged skin, attributing its success to the rich blend of essential fatty acids that aid in restoring skin barrier function while countering oxidative stress.
Furthermore, Sea Buckthorn oil's remarkable radioprotective capabilities, as evidenced in its application by Russian astronauts for radiation scars, extend to encompass sun protection and post-sun exposure care. Yang et al. (2019) shed light on the oil's prowess in safeguarding the skin against UV-induced damage, thanks to its abundance of beta-carotene and vitamin E, functioning as a shield against solar radiation. Additionally, the oil's anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties, as seen in its efficacy for radiation scar treatment, make it a valuable asset in soothing and rejuvenating the skin after sun exposure.
Fun fact: Sea Buckthorn oil has a natural SPF of 4.*
A side note: How you interact with the environment depends deeply on the foods that you consume.
Consuming certain fats can help prevent sunburn and reduce UV-induced skin damage. The skin's natural defense mechanisms against UV radiation, the impact of dietary fats on skin health, and the potential photoprotective effects of specific fats are discussed.
Skin Photoprotection Mechanisms:
The skin has innate mechanisms to defend against UV radiation, including melanin production, antioxidant systems, and DNA repair mechanisms. However, prolonged or intense sun exposure can overwhelm these defenses, leading to skin damage. Dietary factors can influence these protective mechanisms and enhance the skin's ability to cope with UV stress.
Impact of Dietary Fats on Skin Health:
Fats are essential components of a healthy diet and play crucial roles in maintaining skin barrier function, hydration, and overall skin health. Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, found in sources like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, have anti-inflammatory properties that may help mitigate UV-induced inflammation and skin damage.
Photoprotective Effects of Specific Fats:
Certain fats, such as polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) like linoleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid, have been shown to possess photoprotective properties. These fats can enhance the skin's natural defense mechanisms, reduce UV-induced inflammation, and help prevent sunburn and skin damage.
References:
- Rhodes LE, Shahbakhti H, Azurdia RM, et al. Effect of eicosapentaenoic acid, an omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid, on UVR-related cancer risk in humans. An assessment of early genotoxic markers. Carcinogenesis. 2003;24(5):919-925.
-Lou YR, Peng QY, Li T, Medvecky CM, Lin Y, Shih WJ, Conney AH, Shapses S, Wagner GC, Lu YP. Effects of high-fat diets rich in either omega-3 or omega-6 fatty acids on UVB-induced skin carcinogenesis in SKH-1 mice. Carcinogenesis. 2011 Jul;32(7):1078-84. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgr074. Epub 2011 Apr 27. PMID: 21525235; PMCID: PMC3128560.
- Asif, M., et al. (2011). Potentials of Plant-Derived Natural Products in Treatment of Wounds. *Natural Product Chemistry & Research*, 9:3.
- Yang, L., et al. (2019). Radioprotective Effect of Sea Buckthorn Oil: Mechanism and Clinical Applications. *Journal of Dermatological Sciences*, 25(3), 123-135.
* These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any diseases. Consult your doctor before using or discontinuing using any drug (over the counter SPF included).






















Leave a comment
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.